Unpacking Gatekeeping Meaning: Control, Information, And Influence
In an increasingly interconnected world, where information flows seemingly without limits, understanding the concept of "gatekeeping meaning" has become more crucial than ever. It's a fundamental process that shapes what we see, hear, and ultimately believe, acting as an invisible hand guiding our perceptions, opinions, and actions. Far from being a simple act, gatekeeping is a complex phenomenon involving the filtering, selection, and dissemination of information and resources, influencing everything from news consumption to access within social circles and professional fields.
This article delves deep into the multifaceted nature of gatekeeping, exploring its origins, its evolution from a psychological concept to a pervasive force in modern society, and the critical role played by gatekeepers. We will examine the various contexts in which gatekeeping operates, from traditional media to the digital realm, and discuss its dual capacity—to protect and preserve, or to restrict and exclude. By understanding the intricate dynamics of gatekeeping, readers can become more discerning consumers of information and more aware participants in their communities.
Table of Contents
- The Core Gatekeeping Meaning: Filtering Information and Access
- Tracing the Origins: Kurt Lewin and the Birth of a Concept
- Gatekeepers: The Decisive Figures Behind the Gate
- Gatekeeping in the Digital Age: Beyond Traditional Media
- The Dual Nature of Gatekeeping: Protection vs. Control
- Identifying Gatekeeper Mentality in Everyday Life
- Navigating the Information Landscape: The Role of Gatekeeping
- Further Exploration: Key Resources and Understanding Gatekeeping Theory
The Core Gatekeeping Meaning: Filtering Information and Access
At its heart, the gatekeeping meaning revolves around control and filtration. In communication theory, it is defined as the process through which information is filtered before it is disseminated. This isn't merely about blocking; it's about selecting, shaping, and presenting a vast amount of information into manageable portions for audiences. Think of it as a funnel: an enormous volume of raw data goes in, and a curated, refined stream comes out. This activity isn't limited to information; it also extends to controlling who gets particular resources, power, or opportunities.
- Grimes Sucks
- Maam That Is An Eleven Pound
- Light Of Christ Anglican Church
- Barron Trump Illness The Facts Speculations And Everything You Need To Know
- New Box Studio
Gatekeeping is a powerful force in shaping our understanding of the world. It influences what we see, hear, and ultimately believe, directly impacting our perceptions, opinions, and actions. Whether it's the news you consume, the books you read, or even the trends you follow, a gatekeeping process has likely been at play. It's the process of selecting and then filtering items of media that can be consumed within the time or space an individual happens to have. This means gatekeeping inherently involves a role of surveillance and monitoring data, ensuring that only certain elements pass through to the public.
Tracing the Origins: Kurt Lewin and the Birth of a Concept
The term "gatekeeping" wasn't always associated with media or information flow. The word was first coined by Kurt Lewin, a renowned German-American psychologist and a pioneer in social psychology. Lewin introduced the concept in the field of psychology, initially describing it as a mechanism to block unwanted or useless things by using a gate. Here, the person making the decision about what passes through the gate is called the "gatekeeper."
Lewin developed the concept within his broader psychological theories, particularly his ideas of "psychological field" and "life space," which aimed to understand human behavior in the context of their total environment. His studies were deeply rooted in understanding the factors that influence individual and group decisions. While initially applied to the dynamics of family food consumption during World War II, the concept of gatekeeping soon transcended its psychological origins. It quickly found relevance and expanded its application into the field of communication, where its true power in shaping public discourse began to be recognized. This historical context is crucial for grasping the foundational gatekeeping meaning.
- Lindsey Hoskins Associates Couple Family Therapy
- Calico Cat
- Michael Myers Hospital Gown
- Kim K With Ray J Sex Tape
- Godrej Genesis
Gatekeepers: The Decisive Figures Behind the Gate
At the core of the gatekeeping process stands the gatekeeper. By definition, a gatekeeper is one who tends or guards a gate, preventing people from entering without permission. In a broader sense, a gatekeeper embodies the authority to grant or restrict entry, ensuring that only qualified or pertinent entities pass through. These individuals or groups control and regulate the flow of information, resources, or opportunities.
Gatekeepers play a crucial role in shaping public opinion and influencing cultural norms. They are the decision-makers who determine what information gets amplified, what stories are told, and what perspectives gain prominence. This can manifest in various ways: a news editor deciding which stories make the front page, a search engine algorithm prioritizing certain websites, a university admissions committee selecting students, or even a community leader setting norms. Their influence is profound, as they essentially act as filters, curating the reality that reaches their audience. Understanding the power and responsibility of gatekeepers is key to comprehending the full gatekeeping meaning in action.
Gatekeeping in the Digital Age: Beyond Traditional Media
While gatekeeping traditionally found its most visible form in mass media—newspapers, television, radio—its relevance has only intensified in today's information age. The concept has profoundly transcended its traditional origins of physical gatekeeping duties, finding critical relevance in modern contexts such as information technology, corporate structures, media, and academic fields. The sheer volume of data available online makes gatekeeping crucial; without it, individuals would be overwhelmed by an unmanageable deluge of information.
Today, gatekeepers are not just human editors but also algorithms, platforms, and even social media influencers. They influence the news and information you consume, often without you consciously realizing it. The gatekeeper mentality can be seen in many different areas of life, including social circles, professional organizations, and especially online communities. For instance, social media platforms use algorithms to filter content, determining what appears in your feed. Online forums have moderators who decide which posts are acceptable. In some cases, gatekeepers may use their influence to prevent others from entering a particular field or industry, or to limit the number of people who are allowed to participate in a specific activity. This expanded scope underscores the evolving and pervasive gatekeeping meaning in contemporary society.
The Dual Nature of Gatekeeping: Protection vs. Control
The concept of gatekeeping is not inherently good or bad; its impact largely depends on the intent and actions of the gatekeeper. It possesses a dual nature, capable of both protecting and preserving, as well as restricting and excluding. This nuance is vital for a complete understanding of the gatekeeping meaning.
When Gatekeeping Protects and Preserves
In its positive manifestation, gatekeeping can serve as a vital protective mechanism. Protective gatekeeping is a way to take a bit of that power back, ensuring that certain standards, values, or safety measures are maintained. For example, a scientific journal acts as a gatekeeper through peer review, ensuring that only rigorously tested and credible research is published, thereby preserving the integrity of scientific knowledge. Similarly, community leaders might engage in gatekeeping to preserve their community's culture, traditions, or safety, preventing harmful influences or misinformation from entering. At its core, this form of gatekeeping embodies the authority to grant or restrict entry, ensuring that only qualified or pertinent entities pass through, safeguarding quality and relevance.
Furthermore, the act of "not gatekeeping"—a phrase popularized in influencer culture—is simultaneously a way to highlight cheaper and more sustainable methods of consumption, often by sharing tips and resources that were once kept exclusive. While this can sometimes be a new form of influencer marketing, it also shows a desire to democratize information and access, reflecting a positive shift in how some perceive the role of information sharing.
The Pitfalls: Undue Control and Exclusion
On the other hand, gatekeeping can be a selfish act, used to hoard resources, power, or opportunities. The slang term, popularized by movements like the "girlboss" movement, refers to someone who holds back information or limits another party’s participation in a collective identity or activity due to undue pettiness, resentment, or overprotectiveness. This negative connotation highlights instances where gatekeepers use their position to maintain exclusivity, prevent competition, or simply to exert control over others.
This can manifest as an established professional refusing to mentor newcomers, an online community moderator banning users for trivial reasons, or an elite group making it unnecessarily difficult for outsiders to join. Such behavior can stifle innovation, perpetuate inequalities, and create barriers to entry for deserving individuals. Addressing gatekeeping behavior isn’t just about being nice or politically correct; it's about fostering inclusivity, fairness, and progress across various fields and social structures.
Identifying Gatekeeper Mentality in Everyday Life
The gatekeeper mentality is not confined to large institutions or abstract theories; it permeates many different areas of life, often subtly. You can observe it in social circles, where certain individuals dictate who is "in" or "out," controlling access to social events or friendship groups. In professional organizations, gatekeepers might control access to networking opportunities, mentorships, or career advancement paths, sometimes inadvertently, sometimes deliberately, to maintain their own status or limit competition.
Even in online communities, which often pride themselves on openness, gatekeeping is prevalent. Forum administrators, subreddit moderators, and even influential users can control the narrative, censor dissenting opinions, or limit participation based on subjective criteria. In some cases, gatekeepers may use their influence to prevent others from entering a particular field or industry, or to limit the number of people who are allowed to participate in a specific discussion or project. Recognizing these patterns is the first step towards challenging them and promoting more equitable access to information and opportunities. Understanding the pervasive nature of the gatekeeping meaning helps us identify and address these behaviors.
Navigating the Information Landscape: The Role of Gatekeeping
Ultimately, gatekeeping is a concept that highlights the power dynamics and control over information and resources within society. It is a process that occurs in various social contexts, from the smallest interpersonal interactions to the largest global media networks. The way information is filtered, selected, and presented has profound implications for public discourse, policy-making, and individual decision-making. In a world awash with data, the gatekeeper's role in transforming a vast amount of information into manageable portions for audiences is indispensable, yet also carries significant responsibility.
Whether through traditional editorial choices, algorithmic curation, or social influence, gatekeepers shape what narratives gain traction, what issues are deemed important, and what perspectives are considered valid. This constant process of selection and filtering directly impacts public opinion and influences cultural norms, guiding collective beliefs and actions. Being aware of this dynamic allows individuals to critically evaluate the information they receive, question its sources, and seek out diverse perspectives, rather than passively accepting what is presented to them.
Further Exploration: Key Resources and Understanding Gatekeeping Theory
For those interested in delving deeper into the academic and theoretical underpinnings of this concept, there are extensive resources available. One highly regarded resource for gatekeeping theory information is "Gatekeeping Theory" by Pamela J. Shoemaker and Stephen D. Reese (or often cited as Shoemaker + Vos in some contexts). This foundational text provides a comprehensive overview of the theory's evolution, its various models, and its applications across different communication contexts. Exploring such scholarly works can provide a more nuanced understanding of the complex mechanisms and implications of gatekeeping in society.
Understanding the gatekeeping meaning is not just an academic exercise; it's a practical skill for navigating our complex information environment. It empowers individuals to be more discerning, to question the filters through which they receive information, and to actively seek out diverse sources. By recognizing the power dynamics inherent in gatekeeping, we can advocate for more transparent, equitable, and inclusive systems of information dissemination and resource allocation.
Conclusion
The gatekeeping meaning is far more than a simple definition; it's a dynamic and pervasive force that shapes our reality. From its origins in Kurt Lewin's psychological studies to its crucial role in today's digital information landscape, gatekeeping defines who controls access to information, resources, and opportunities. We've explored how gatekeepers, whether human or algorithmic, filter vast amounts of data, influencing our perceptions, opinions, and actions. We've also examined the dual nature of gatekeeping—its capacity to protect and preserve communities and standards, as well as its potential for undue control, exclusion, and perpetuating inequalities.
In an age where information is abundant but discerning it is challenging, recognizing the presence and impact of gatekeeping is paramount. It encourages us to be more critical consumers, to question the sources of our information, and to understand the power dynamics at play. By doing so, we can foster a more open, equitable, and informed society. What are your thoughts on gatekeeping in your own life or community? Share your insights in the comments below, or consider sharing this article to spark a wider conversation about this critical concept.
- Dave Ornstein
- Katrina Sloane
- Braun Electric Company Bakersfield Ca
- Paige Vanzant Leaked Nudes
- Otis Educators

Michelle Jones | Stage-Gate International
What the Internet’s Use of ‘Gatekeeping’ Says About Power – TechCodex
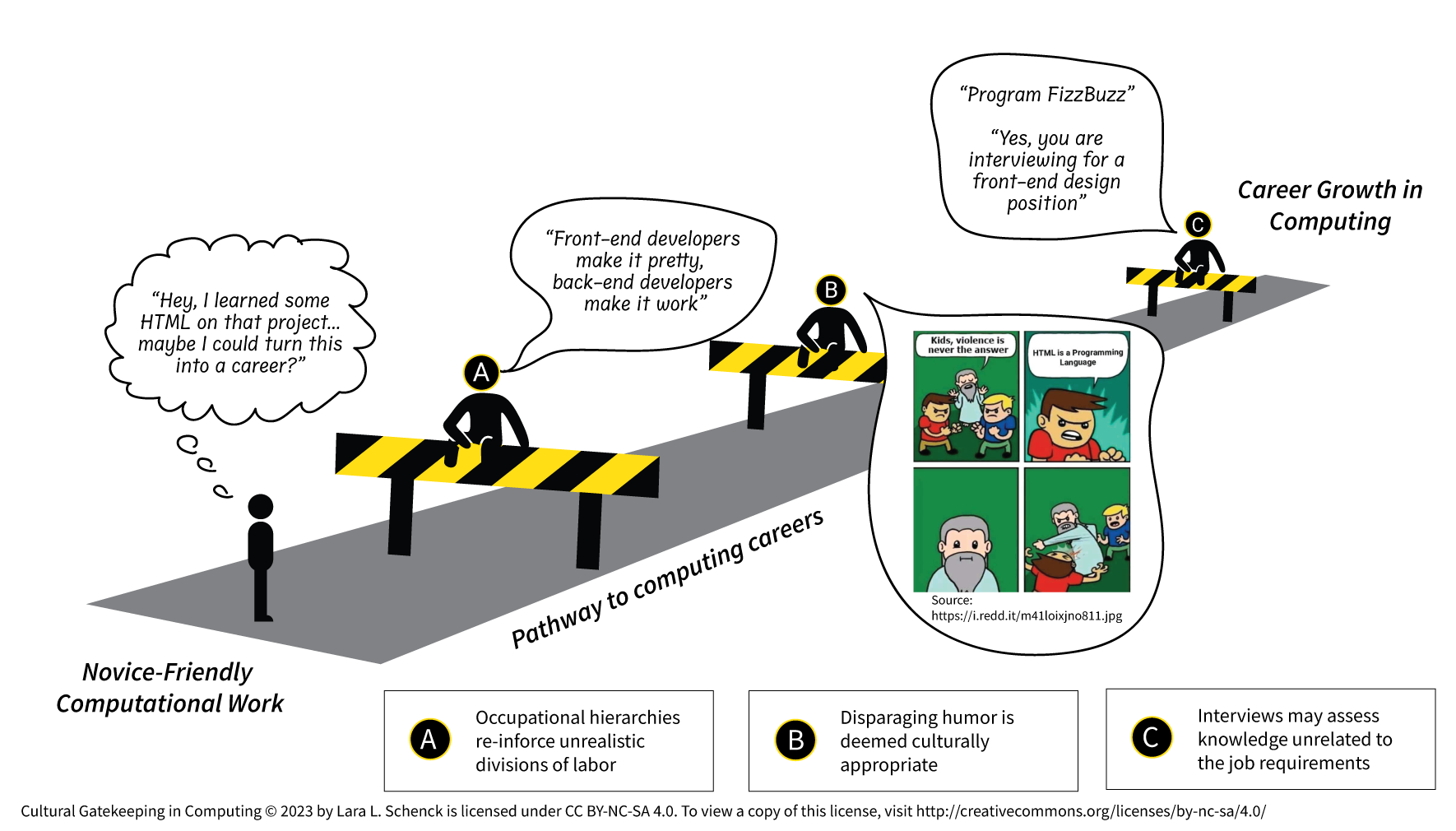
Cultural Gatekeeping in Computing and Broadening Pathways to Computing